- Published on
Biotechnology in Agriculture Feeding the Future
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
The world's population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, putting immense pressure on the agricultural sector to produce more food. Climate change, soil degradation, and water scarcity further exacerbate the challenge. Biotechnology in agriculture offers a beacon of hope in addressing these concerns. This article delves into the applications, benefits, and future prospects of biotechnology in agriculture, highlighting its potential to feed the future sustainably.

- Understanding Biotechnology in Agriculture
- Applications of Biotechnology in Agriculture
- Benefits and Challenges
- Conclusion
- Call to Action
Understanding Biotechnology in Agriculture
Biotechnology in agriculture involves the application of biological systems, living organisms, or derivatives thereof, to improve crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content. This includes genetic engineering, marker-assisted breeding, and microbials. By manipulating the genetic code of crops, scientists can introduce desirable traits, such as:
- Insect resistance, reducing the need for pesticides
- Drought tolerance, enabling crops to thrive in water-scarce conditions
- Enhanced nutritional content, improving human health
# Example of a genetic engineering code snippet
from Bio import SeqIO
record = SeqIO.read("gene_of_interest.fasta", "fasta")
print(record.seq) # Output: The DNA sequence of the gene of interest
Applications of Biotechnology in Agriculture
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses biotechnology to develop crops that are more resilient and responsive to environmental conditions. This includes:
- Drought-tolerant crops, such as corn and soybeans
- Insect-resistant crops, reducing the need for pesticides
- Nutrient-rich crops, enhancing human health

2. Biotech Crops
Biotech crops are genetically modified to possess desirable traits. Examples include:
- Golden Rice, enriched with beta-carotene to combat vitamin A deficiency
- Insect-resistant corn, reducing pesticide use
- Herbicide-tolerant soybeans, simplifying weed control
# Example of a biotech crop simulation
import numpy as np
def crop_yield(simulation_days, weather_data):
# Simulate crop growth and yield based on weather data
return np.random.normal(0, 1, simulation_days)
print(crop_yield(30, [20, 25, 30, 25, 20])) # Output: Simulated crop yield data
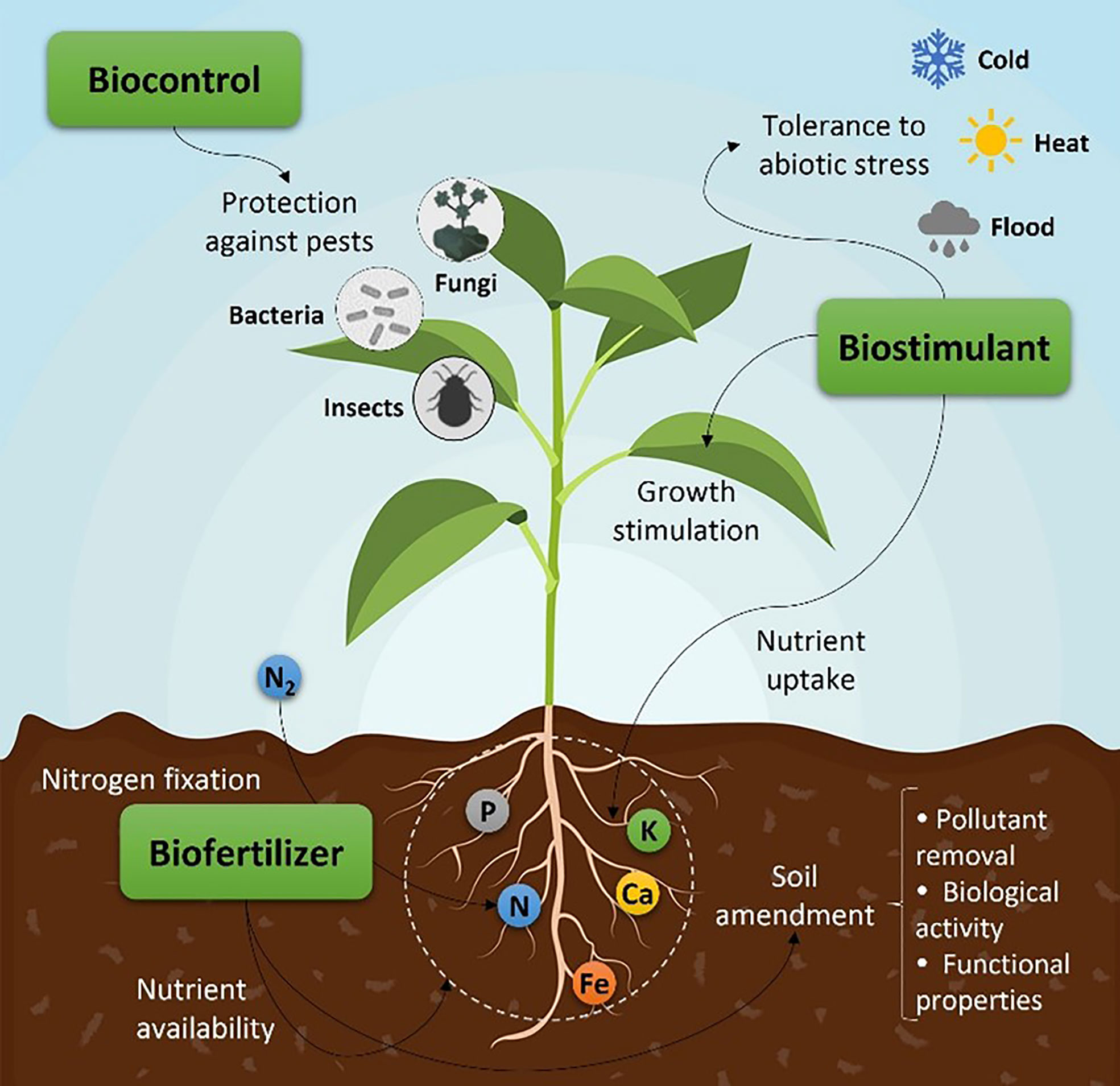
3. Microbial Applications
Microbials play a crucial role in soil health, nutrient cycling, and plant growth promotion. Biotechnology enables the development of:
- Biofertilizers, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers
- Biopesticides, providing an alternative to chemical pesticides
- Soil microbiome engineering, enhancing soil fertility and structure
Benefits and Challenges
Biotechnology in agriculture offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased crop yields and productivity
- Improved nutritional content and human health
- Reduced environmental impact and pesticide use
- Enhanced sustainability and food security
However, challenges persist, such as:
- Public perception and acceptance of genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
- Regulatory frameworks and patenting issues
- Ensuring equitable access to biotech crops for small-scale farmers
# Example of a benefits and challenges table
| **Benefits** | **Challenges** |
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------- |
| Increased crop yields | Public perception of GMOs |
| Improved nutritional content | Regulatory frameworks |
| Reduced environmental impact | Ensuring equitable access |
Conclusion
Biotechnology in agriculture holds the key to feeding the future sustainably. By embracing biotech crops, precision agriculture, and microbial applications, we can increase crop yields, reduce environmental impact, and enhance human health. However, it's essential to address the challenges and concerns surrounding biotechnology in agriculture.
Call to Action
As we move forward, it's crucial to engage in open discussions, foster education, and promote collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and farmers. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of biotechnology in agriculture, ensuring a food-secure and sustainable future for generations to come.
"Feeding the future sustainably requires a convergence of innovation, policy, and collective action. Let's work together to harness the power of biotechnology in agriculture."
