- Published on
Building RESTful APIs with Spring and API Gateway A Hands-On Guide
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
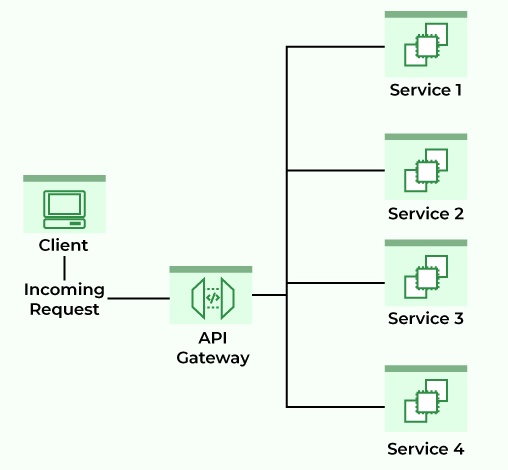
Building robust, scalable RESTful APIs is a core aspect of modern backend development. Using Spring Boot and integrating with an API Gateway empowers developers to create modular, maintainable microservices architectures while centralizing concerns like authentication and request routing.
- Setting Up a Spring Boot RESTful API
- Designing and Implementing the API Gateway
- Integrating Security and Advanced Features
- Conclusion
- Take the Next Step!
Setting Up a Spring Boot RESTful API
Spring Boot provides a rapid way to build RESTful web services with minimal upfront configuration. Let’s scaffold a simple user service.
// UserController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {
User user = userService.findUserById(id);
return ResponseEntity.ok(user);
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
User created = userService.saveUser(user);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(created);
}
}
In this example:
- The
@RestControllerand@RequestMappingannotations make exposing JSON endpoints straightforward. - Typical REST verbs (
GET,POST, etc.) map to Java methods.

Designing and Implementing the API Gateway
An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests, handling tasks such as routing, authentication, rate limiting, and transformation. Spring Cloud Gateway is a popular choice for Spring-based ecosystems.
# application.yml for Spring Cloud Gateway
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-service
uri: http://localhost:8081
predicates:
- Path=/api/users/**
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20
This configuration:
- Routes
/api/users/**traffic to the user service. - Applies basic rate limiting to enhance stability and security.

Integrating Security and Advanced Features
API Gateways are ideally suited for enforcing cross-cutting concerns like authentication and logging. Here’s how you might secure routes using JWT tokens with Spring Cloud Gateway.
// Custom filter for JWT authentication
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter implements GatewayFilterFactory<JwtAuthenticationFilter.Config> {
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
return (exchange, chain) -> {
// Extract and validate JWT
String token = exchange.getRequest()
.getHeaders()
.getFirst(HttpHeaders.AUTHORIZATION);
if (token == null || !isValidToken(token)) {
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
};
}
}
Other enhancements you can add:
- Centralized monitoring and logging with tools like Spring Cloud Sleuth
- Circuit breaking with Resilience4j
- Request/response transformation
Conclusion
Developing RESTful APIs with Spring Boot, and exposing them securely and efficiently via an API Gateway, forms the backbone of a scalable microservices architecture. By leveraging these tools, you simplify service management, improve maintainability, and empower teams to build forward-thinking applications.
Take the Next Step!
Start building your own microservices ecosystem with Spring Boot and API Gateway today. Explore further features like distributed tracing, service discovery, and more advanced security to take your APIs to the next level.
