- Published on
Building Scalable Serverless Applications with AWS Lambda
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
Serverless computing has revolutionized how developers design and deploy modern applications—removing the burden of infrastructure management and allowing teams to focus on writing code. AWS Lambda stands at the forefront of this paradigm, enabling scalable, event-driven applications by executing your code in response to triggers, all without provisioning or managing servers.

- Core Concepts of AWS Lambda and Serverless Architecture
- Integrating Lambda with Other AWS Services
- Patterns and Best Practices for Scalable Serverless Systems
- Conclusion
- Take the Next Step with Serverless
Core Concepts of AWS Lambda and Serverless Architecture
At its heart, AWS Lambda lets you run backend code in response to events, such as HTTP requests, file uploads, or queue messages—charging you only for actual compute time used.
- Event-driven execution: Functions are triggered automatically by events from AWS services or custom sources.
- No server management: AWS handles infrastructure, scaling, and fault tolerance.
- Stateless design: Each Lambda invocation is independent, ideal for microservices and distributed systems.
A basic handler function in Python looks like:
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Event received:", event)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Hello from AWS Lambda!'
}
This simplicity scales from basic automation to complex backend services—making Lambda highly versatile.
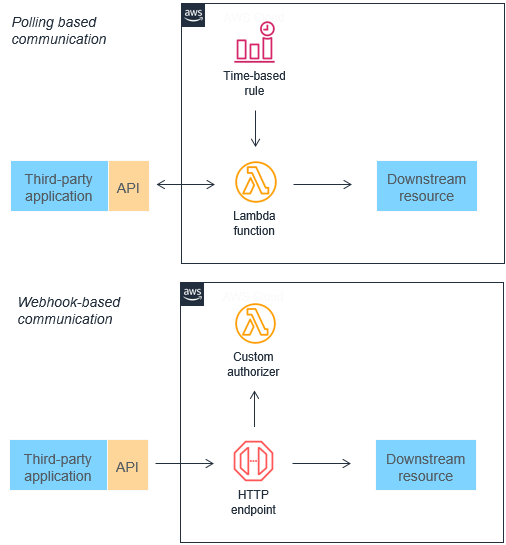
Integrating Lambda with Other AWS Services
The real power of serverless emerges when Lambda interacts seamlessly with other AWS services, forming robust application backends.
Triggering Lambda Functions
- API Gateway: Build serverless APIs by linking REST endpoints to Lambda handlers.
- S3: Automatically process uploaded files or images.
- DynamoDB Streams: React to database changes for real-time processing.
Example: Setting up an AWS Lambda function triggered by S3 file upload (Node.js):
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const bucket = event.Records[0].s3.bucket.name
const key = event.Records[0].s3.object.key
console.log(`File uploaded: ${key} in bucket ${bucket}`)
// Add your S3 processing logic here
return { statusCode: 200 }
}
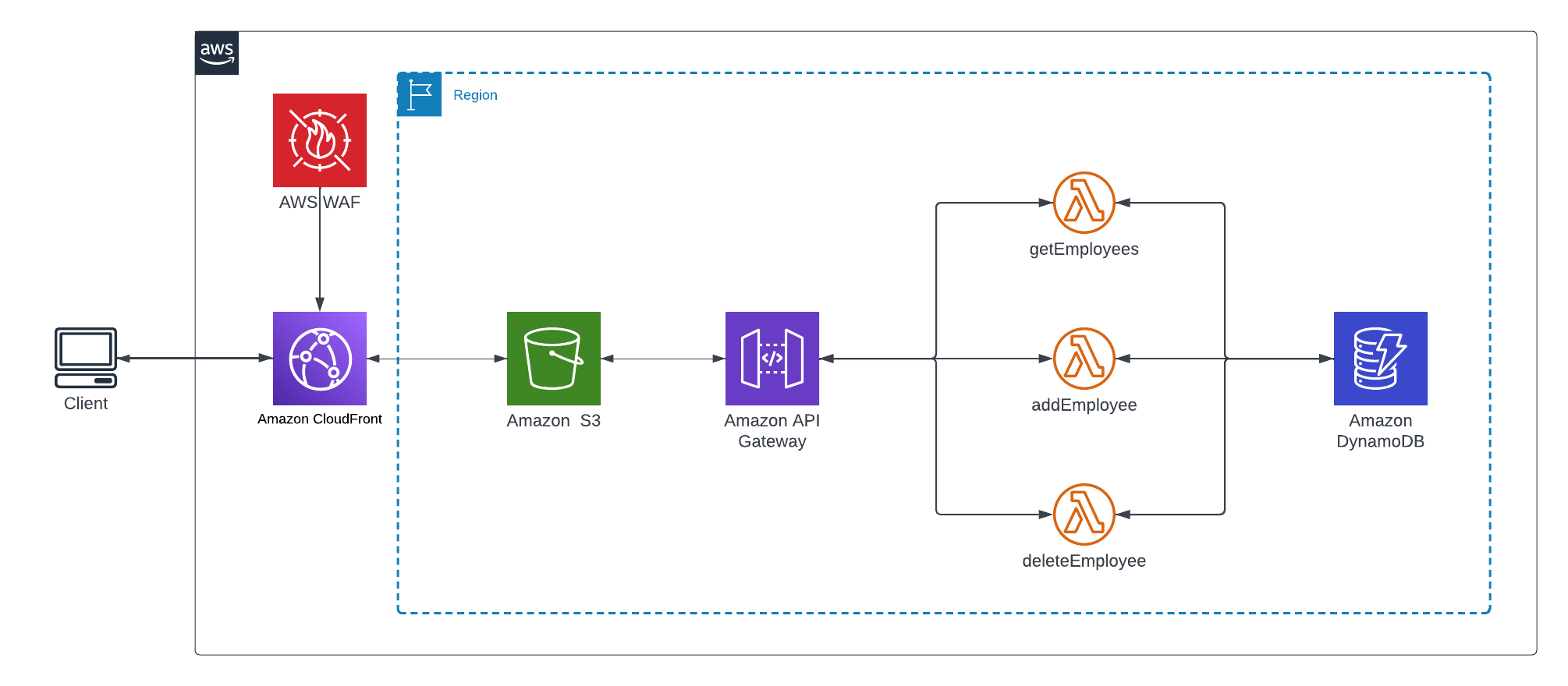
Patterns and Best Practices for Scalable Serverless Systems
Building real-world Lambda-backed systems requires leveraging proven patterns and practical tips:
Key Serverless Patterns
- Microservices decomposition: Implement business logic in small, independent Lambda functions.
- Event-driven pipelines: Orchestrate workflows using AWS Step Functions for stateful, multi-step logic.
- Fan-out processing: Use SNS or EventBridge to distribute events to multiple Lambda functions.
Best Practices
- Keep functions single-responsibility and stateless.
- Minimize cold starts by optimizing package size and using Provisioned Concurrency for latency-sensitive workloads.
- Secure functions with IAM roles scoped by least privilege.
- Centralize logging and monitoring with AWS CloudWatch.
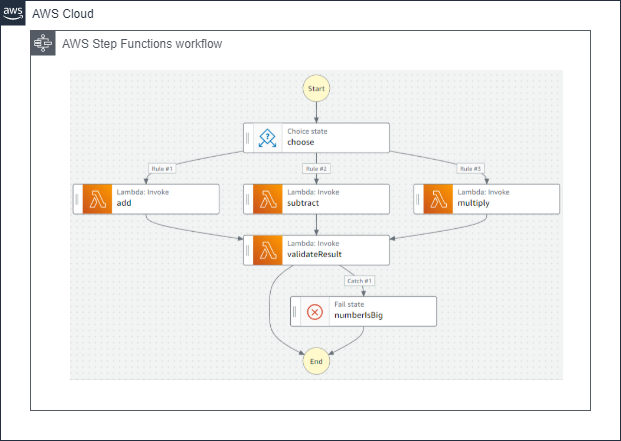
Example: Using AWS Step Functions to orchestrate a serverless workflow (ASL JSON snippet):
{
"StartAt": "FirstTask",
"States": {
"FirstTask": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:region:acct-id:function:FirstLambda",
"Next": "SecondTask"
},
"SecondTask": {
"Type": "Task",
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:region:acct-id:function:SecondLambda",
"End": true
}
}
}
Conclusion
AWS Lambda empowers teams to build highly scalable, event-driven systems without the complexity of server management. By combining Lambda with other AWS services and following best practices, you can architect robust, maintainable, and cost-effective applications that can scale effortlessly from prototype to production workload.
Take the Next Step with Serverless
Ready to build your own serverless backend? Start experimenting with Lambda triggers, try integrating services like S3 and DynamoDB, and explore powerful orchestration with AWS Step Functions to unlock the full power of serverless applications on AWS!
