- Published on
Mastering Ansible Automation and Configuration Management Made Easy
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced IT landscape, efficient automation and configuration management are essential for maintaining reliable and scalable infrastructure. Ansible has rapidly gained popularity as a simple yet powerful open-source tool that helps teams automate repetitive tasks, enforce consistency, and accelerate software delivery. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced DevOps engineer, mastering Ansible can dramatically boost your productivity and infrastructure reliability.

- Understanding Ansible: Core Concepts
- Automating Common Operations
- Advanced Configuration Management
- Conclusion
- Ready to Automate with Ansible?
Understanding Ansible: Core Concepts
Ansible operates by connecting to your servers via SSH (or WinRM for Windows) and executing tasks using simple human-readable YAML files called playbooks. It follows an agentless model, requiring no special software to be installed on managed nodes.
- Inventory: A list of hosts to manage
- Modules: Units of work encapsulating reusable logic (e.g.,
yum,service) - Playbooks: YAML files describing automation workflows
# A simple Ansible playbook example
- name: Install and start Apache
hosts: webservers
become: true
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: Ensure httpd is running
service:
name: httpd
state: started
With Ansible, you can abstract complex operations into succinct, version-controlled files that are easy to audit and share.
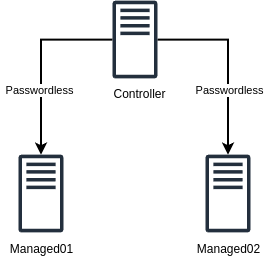
Automating Common Operations
Ansible excels at automating routine tasks, from provisioning servers to deploying applications. Modules exist for most critical system operations, enabling smooth orchestration with minimal effort.
- User Management: Create or remove users across infrastructure
- Package Installation: Manage OS packages consistently
- Service Control: Start, stop, and enable services
# Example: Create a user and deploy an SSH key
- name: Add DevOps user with SSH key
hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Ensure 'devops' user exists
user:
name: devops
state: present
- name: Add authorized SSH key for 'devops'
authorized_key:
user: devops
key: "{{ lookup('file', 'devops_id_rsa.pub') }}"
Automation with Ansible dramatically reduces manual effort, human error, and onboarding time for new team members.
Advanced Configuration Management
Beyond simple automation, Ansible empowers teams to codify configuration states and enforce them across environments. Features like variables, roles, and templates make it easy to create flexible, reusable configurations.
- Variables & Templates: Parameterize playbooks for different environments
- Roles: Modularize tasks and handlers for reuse
- Idempotency: Ensures repeated runs yield the same result
# Example: Using templates for dynamic configuration
- name: Configure NGINX with template
hosts: webservers
become: true
vars:
server_name: 'my-app.example.com'
tasks:
- name: Deploy custom nginx.conf
template:
src: nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: Restart NGINX
handlers:
- name: Restart NGINX
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
Templates use Jinja2, allowing dynamic generation of configuration files tailored to each environment or host.
Conclusion
Ansible empowers organizations to automate repetitive tasks, enforce configuration standards, and enhance collaboration across development and operations. Its agentless, readable, and modular design makes it a top choice for modern infrastructure management. By leveraging Ansible’s features—from playbooks to roles and templates—you can streamline your IT operations and focus more on innovation.
Ready to Automate with Ansible?
Start with a small project, experiment with playbooks, and watch your infrastructure management evolve. For deeper exploration, check out the official Ansible documentation and join the vibrant community to share tips and best practices!
