- Published on
Mastering Kubernetes A Comprehensive Guide to Container Orchestration and Management
- Authors

- Name
- Adil ABBADI
Introduction
Kubernetes has redefined how modern applications are deployed, managed, and scaled in complex cloud environments. As the cornerstone of container orchestration, it empowers developers and DevOps engineers alike to automate deployment, scaling, and operation of containerized workloads efficiently. Whether you're just starting out or looking to level up your skills, understanding Kubernetes' orchestration capabilities is essential in today's tech landscape.
- Understanding Kubernetes Architecture
- Deploying and Managing Containers with Kubernetes
- Scaling and Self-Healing Workloads
- Advanced Orchestration: Networking, Storage, and Services
- Conclusion
- Ready to Orchestrate Your Applications?
Understanding Kubernetes Architecture
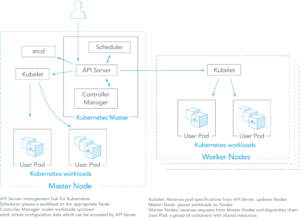
Kubernetes is composed of several key components working seamlessly to manage containers and maintain desired system states. Its architecture is designed to ensure both high availability and scalability.
At a high level, Kubernetes clusters consist of:
- Master Node(s): Responsible for cluster coordination, maintaining records, and scheduling workloads.
- Worker Node(s): Run the actual application containers.
- Key Components:
kube-apiserverfor API communicationetcdfor persistent storagekube-schedulerfor workload distributionkubeletfor node managementkube-proxyfor networking
# Sample Kubernetes cluster definition (minified)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: nginx:1.25
The above YAML defines a simple Pod, which is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, running an Nginx container.
Deploying and Managing Containers with Kubernetes
Kubernetes manages application deployment through declarative configurations. This enables users to specify the desired state, and Kubernetes takes care of making it reality.

Pods and Deployments
- Pods: The basic unit, encapsulating one or more containers.
- Deployments: Controller objects that manage the lifecycle of Pods, enabling updates, scaling, and rollback.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.25
The deployment manifest above ensures three Nginx pods run at all times, automatically replacing failed pods and enabling seamless updates.
Scaling and Self-Healing Workloads
One of Kubernetes’ greatest strengths lies in its ability to automatically scale applications and recover from failures, ensuring high availability.

Horizontal Pod Autoscaling
Kubernetes can dynamically adjust the number of pod replicas based on CPU usage or other select metrics using the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA).
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nginx-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: my-nginx-deployment
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
With this configuration, Kubernetes auto-scales the number of Nginx pods to maintain CPU utilization around 50%.
Advanced Orchestration: Networking, Storage, and Services
A production-grade Kubernetes setup handles networking, storage, and service discovery gracefully, unlocking truly resilient and flexible application platforms.

Services for Discovery and Load Balancing
Kubernetes Services enable stable networking endpoints to pods, with load balancing, discovery, and IP abstraction.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
This example exposes an Nginx deployment using a Service, allowing external traffic to be load-balanced to healthy pods.
Persistent Storage with Volumes
For stateful applications, Kubernetes supports persistent volume management.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nginx-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
This lets you attach durable storage to your containers, decoupling state from lifecycle.
Conclusion
Kubernetes streamlines the operation of modern cloud-native applications, automating the deployment, scaling, networking, and storage of containers in a reliable manner. Mastering its orchestration principles empowers teams to build resilient, self-healing, and scalable infrastructure with confidence.
Ready to Orchestrate Your Applications?
Start experimenting with Kubernetes today using local tools like minikube or kind, and watch as your containerized workloads take flight at scale!
